With tools like asset management software and integrated depreciation tracking, organizations can manage depreciation seamlessly and improve reporting accuracy. Then there’s units of https://www.bookstime.com/articles/fractional-cfo production, which ties depreciation to how much the asset is actually used—a great option if usage varies significantly. Sum-of-the-years’ digits is a bit more complex, offering a depreciation rate that changes each year, based on a digits method where you calculate the sum of the asset’s remaining lifespan. When reporting, list the asset under property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) at its original purchase price.
- So, the accumulated depreciation for the equipment after 3 years would be $6,000.
- Cost of Goods Sold is a general ledger account under the perpetual inventory system.
- Cost of goods sold is usually the largest expense on the income statement of a company selling products or goods.
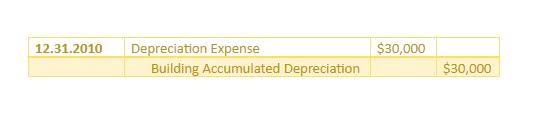
- Accumulated depreciation reports the amount of depreciation that has been recorded from the time an asset was acquired until the date of the balance sheet.
CAPITAL CITY TRAINING LTD
However, before computing the gain or loss, it is necessary to record the asset’s depreciation right up to the moment of the sale. The “sum-of-the-years’-digits” refers to adding the digits in the years of an asset’s useful life. For example, if an asset has a useful life of 5 years, the sum of the digits 1 through 5 is equal to 15 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5). After the financial statements are distributed, it is reasonable to learn that some actual amounts are different from the estimated amounts that were included in the financial statements. We will illustrate the details of depreciation, and specifically the straight-line depreciation method, with the following example. For example, a logistics company managing a fleet of vehicles can use software to track depreciation across multiple assets, ensuring compliance and accuracy.

SERVICES
The naming convention is just different depending on the nature of the asset. For tangible assets such as property or plant and equipment, it is referred to as depreciation. Without proper tracking of assets and depreciation, companies may report inflated asset values, leading to misleading financial statements. You might opt for a declining balance method, front-loading the depreciation to match its heavy use in your business operations.
Depreciation and Taxes

Accountants use the straight line depreciation method because it is the easiest to compute and can be applied to all long-term assets. However, the straight line method does not accurately reflect the difference in usage of an asset and may not be the most appropriate value calculation method for some depreciable assets. Accumulated depreciation is the total amount that was depreciated for an asset up to a single point. Each period is added to the opening accumulated depreciation balance, the assets = liabilities + equity depreciation expense recorded in that period. The carrying value of an asset on the balance sheet is the difference between its historical cost and accrued amortisation.

- While a company might spend cash upfront to buy equipment, the depreciation expense appears spread out across multiple financial statements, reflecting how that equipment’s value decreases through use.
- Accumulated depreciation is the total amount of the depreciation expenditure allocated to a particular asset since the asset was used.
- After the financial statements are distributed, it is reasonable to learn that some actual amounts are different from the estimated amounts that were included in the financial statements.
- Is accumulated depreciation waiting for you on the asset side of the balance sheet, or does it lurk among the liabilities?
- Companies use accumulated depreciation to determine when assets need replacement or upgrades, aiding in budgeting and capital expenditure decisions.
- If the revenues come from a secondary activity, they are considered to be nonoperating revenues.
- The system acts as an asset depreciation calculator, automatically updating depreciation schedules and syncing them with financial data.
The double-declining balance method is a form of accelerated depreciation. It means that the asset will be depreciated faster than with the straight line method. The double-declining balance method results in higher depreciation expenses in the beginning of an asset’s life and lower definition of accumulated depreciation depreciation expenses later. This method is used with assets that quickly lose value early in their useful life.
